https://leetcode.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/
Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal - LeetCode
Level up your coding skills and quickly land a job. This is the best place to expand your knowledge and get prepared for your next interview.
leetcode.com
풀이 과정
특정 트리의 전위 순회 결과와 중위 순회 결과를 입력으로 받아서, 원래 트리를 복원시키는 문제이다.
전위, 중위, 후위 순회의 결과중 2가지 정보로 원래 트리를 복원 시킬 수 있다고 알려져있다. 1가지 정보로는 자식 노드가 왼쪽에 붙을지 오른쪽에 붙을지 알 수 없으므로 판별할 수 없다.

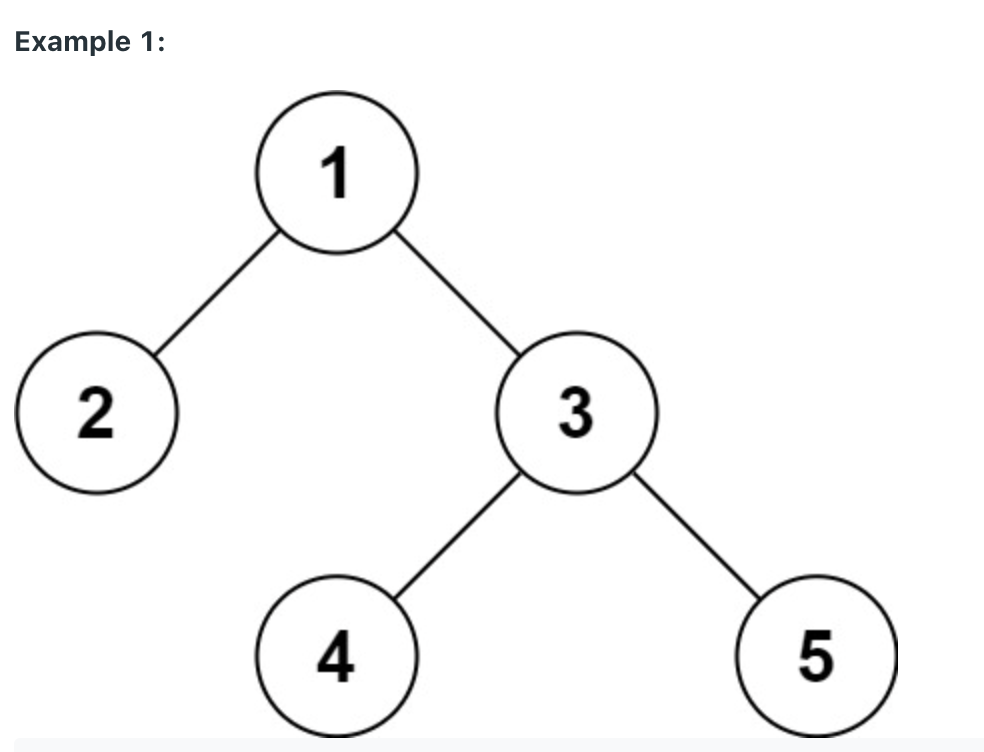
문제에서 보이듯이 이 트리의 전위 순회와 중위 순회 결과는
전위 = [3, 9, 20, 15, 7]
중위 = [9, 3, 15, 20, 7]
이다. 전위 순회의 결과를 앞에서 읽어나가면서 중위 순회의 결과를 읽은 값 기준으로 왼쪽과 오른쪽으로 분할 정복하는 방법으로 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
소스 코드
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if inorder:
index = inorder.index(preorder.pop(0)) # deque의 popleft()를 쓰는게 더 빠름
node = TreeNode(inorder[index])
node.left = self.buildTree(preorder, inorder[0:index])
node.right = self.buildTree(preorder, inorder[index+1:])
return node'알고리즘 문제 풀이 > 리트코드' 카테고리의 다른 글
| LeetCode - 148. Sort List [Python] (0) | 2022.10.17 |
|---|---|
| LeetCode - 215. Kth Largest Element in an Array [Python] (0) | 2022.09.11 |
| LeetCode - 783. Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes [Python] (0) | 2022.09.05 |
| LeetCode - 938. Range Sum of BST [Python] (0) | 2022.09.03 |
| LeetCode - 1038. Binary Search Tree to Greater Sum Tree [Python] (0) | 2022.09.03 |